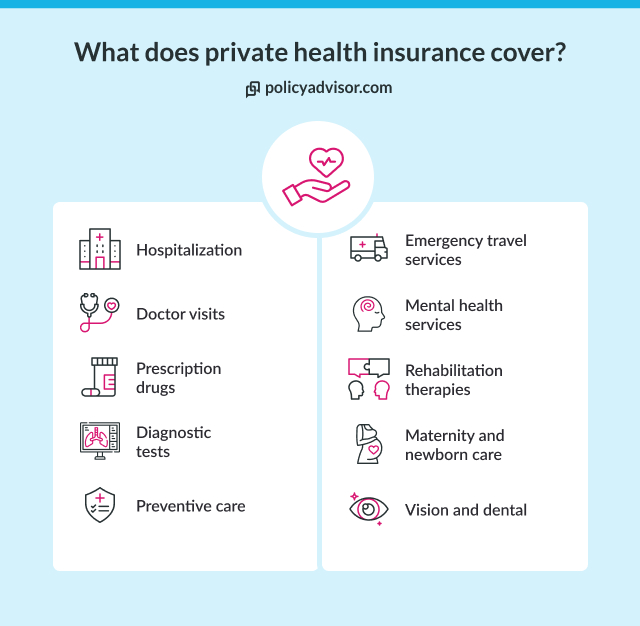
- Private health insurance covers services like dental, vision, and prescription drugs, which are not typically included in provincial health plans
- Plans vary widely and can be customized with add-ons for things like alternative treatments or private hospital rooms
- Most private insurance plans include mental health services such as counseling, which can be essential for comprehensive wellness
- Private plans often include emergency medical coverage for travel outside Canada, a feature not covered by provincial plans
Private health insurance coverage in Canada supplements the public healthcare system and covers services that provincial healthcare plans don’t cover. These services can include prescription medications, dental care, vision care (like eye exams and glasses), and paramedical services such as physiotherapy or chiropractic treatments.
Mental health services, including therapy and counselling, often require private coverage, as do elective cosmetic procedures, private hospital rooms, and ambulance services. Additionally, private health insurance can help cover medical equipment like hearing aids or wheelchairs, as well as provide coverage for emergency medical treatment outside of Canada, which provincial plans do not typically cover.
In this article, we’ll answer key questions about what Canadian private health insurance covers, including specific treatments like pregnancy care, accidents, LASIK, and more.

What are the main differences between public and private health insurance in Canada?
Public health insurance in Canada ensures access to necessary medical care, focusing on hospital and physician services. Personal health insurance covers a wider range of healthcare services and offers more flexibility, such as private hospital rooms and alternative therapies.
Key differences between provincial and personal health insurance in Canada
| Aspect | Public/Provincial health insurance | Private health insurance |
| Coverage scope | Covers medically necessary services, such as doctor visits, hospital stays, and surgeries | Covers additional services like dental, vision, prescription medications, and mental health services |
| Eligibility | Available to all Canadian citizens and permanent residents | Available to individuals who have provincial coverage, and can be accessed either through employer-provided or individually-purchased policies |
| Cost | Free at the point of use (tax-funded), though some provinces may charge premiums | Monthly or annual premiums; additional out-of-pocket costs like deductibles and co-pays may apply |
| Prescription medications | Limited coverage, primarily for seniors and low-income individuals; varies by province | Broader drug coverage, often covering medications not included in public plans |
| Dental and vision care | Generally not covered except for specific cases (e.g., children or low-income seniors) | Often includes dental and vision care, covering routine check-ups, cleanings, eye exams, and sometimes glasses and orthodontics |
| Mental health services | Limited coverage; may include some psychiatric services, but therapy and counseling are often not covered | Includes mental health services such as therapy, counseling, and psychiatric care, though coverage limits vary |
| Hospital room choice | Covers standard ward rooms only | May cover semi-private or private hospital rooms, depending on the policy |
| Alternative healthcare services | Not covered | Can include paramedical services like physiotherapy, chiropractic care, and acupuncture |
| Emergency medical coverage abroad/travel insurance | Not covered | Often includes travel health insurance for medical emergencies outside Canada |
What does a Canadian private health insurance plan look like?
Most Canadian private health insurance plans cover prescription medications, dental and vision care, paramedical services, mental health benefits, emergency travel, medical equipment, hospitalization, etc.
Here’s a sample plan to help you understand how a personal health insurance plan looks:
| Benefit category | Coverage details | Annual coverage limit |
| Prescription medications | Covers 80% of eligible prescription drugs after deductible | Up to $5,000 per year |
| Dental care | Covers routine exams, cleanings, fillings, and extractions | Up to $1,500 per year |
| Vision care | Covers eye exams, prescription glasses, and contact lenses | Up to $300 every 2 years |
| Paramedical services | Covers physiotherapy, chiropractic care, massage therapy, and acupuncture | Up to $500 per service per year |
| Mental health services | Covers therapy, counseling, and psychiatric consultations | Up to $1,000 per year |
| Hospital accommodation | Covers upgrade to semi-private or private room | No annual limit, based on policy |
| Emergency travel | Covers medical expenses for emergencies outside of Canada | Up to $1,000,000 per trip |
| Medical equipment | Covers wheelchairs, walkers, and other medically necessary equipment | Up to $2,000 per year |
| Hearing aids | Covers cost of hearing aids | Up to $500 every 4 years |
*Sample plan with coverage amounts that are indicative and may vary depending on your insurance provider.
Who does your private health insurance cover?
Private health insurance in Canada can cover the policyholder, and their family: spouse and dependent children, depending on the plan type. Individual plans cover only the person who holds the policy, while family plans can extend coverage to spouses and children, often up to a certain age (typically 21-25 if they are full-time students). Some plans also allow additional dependents, such as elderly parents, for an extra premium.
Does health insurance cover pre-existing conditions?
In Canada, coverage for pre-existing conditions in personal health insurance depends on the plan type. Standard personal health plans often exclude or limit pre-existing condition coverage, while replacement and guaranteed issue plans may provide coverage with specific terms.
Replacement plans allow continued coverage if transitioning directly from group insurance, whereas guaranteed issue plans accept all applicants, often with higher premiums or capped benefits.
Does health insurance cover pregnancy?
Yes, private health insurance in Canada may cover pregnancy-related expenses, such as prenatal care, labor and delivery, postnatal care, and complications that arise during pregnancy. Some plans may include coverage for elective procedures like a cesarean section if medically necessary.
However, private health insurance plans typically don’t cover the entire cost of pregnancy-related expenses, and certain aspects, like maternity leave or elective pregnancy-related treatments, might be excluded.
Does health insurance cover accidents?
Yes, accidents are often included in private health insurance policies, covering medical treatment that results from an injury, such as hospitalization, physiotherapy, or rehabilitation services. If you’re injured in an accident, your health insurance will typically cover the medical expenses that arise from the incident.
Such coverage includes hospital stays and treatments that extend beyond what’s covered by provincial health insurance. It’s also important to find out whether your plan includes coverage for medical transportation (e.g., ambulance services), which might not be fully covered by provincial plans.
Does health insurance cover LASIK?
Most private health insurance plans in Canada do not cover LASIK surgery unless it’s medically necessary. LASIK (laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis) surgery, a popular treatment for vision correction, is typically considered an elective procedure.
Some insurers offer additional coverage or riders for elective surgeries like LASIK, while others may exclude it altogether. If LASIK is part of your coverage, you may still face out-of-pocket costs, depending on your plan’s terms.
Does health insurance cover dermatologists?
Yes, dermatological services, including consultations, skin treatments, and procedures, may be covered by private health insurance plans, especially if they are deemed medically necessary (e.g., treatment for skin cancer or severe acne). However, cosmetic dermatological treatments (e.g., Botox, fillers) are typically not covered.
Does health insurance cover cancer?
Yes, cancer treatment, including chemotherapy, radiation, and other necessary medical procedures, is usually covered under private health insurance plans. These plans may also offer coverage for additional services, such as experimental treatments, alternative therapies, and medication that provincial health plans may not fully cover.
Cancer treatment is often expensive, so private insurance can be essential for covering some of the costs associated with specialized care. Coverage for services like home care or palliative care may also be included, depending on the insurer.
What are the limitations and exclusions of private health insurance in Canada?
While private health insurance offers valuable supplementary coverage, it does have several limitations like pre-existing conditions’ coverage, caps in coverage, etc.
- Pre-existing conditions: Many insurers impose waiting periods or exclude coverage for pre-existing conditions
- Coverage caps: Some plans have annual limits on how much they will cover for specific services, which can affect out-of-pocket costs
- Supplementary nature: Private insurance is not a replacement for public healthcare; it is designed to enhance coverage, not substitute the essential services provided by provincial plans
How can I find the best health insurance plan for mental health coverage?
To find the best health insurance plan that includes mental health benefits, we recommend speaking with our advisors. Our team of experienced advisors help you compare plans from 30+ providers in Canada to find you the plan that best meets your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does private health insurance in Canada cover dental and vision care?
Yes, many private health insurance plans cover dental and vision care, though this can vary by plan. Vision care often includes eye exams and prescription glasses or contacts, while dental coverage can include routine check-ups, cleanings, and more specialized treatments.
Does personal health insurance cover mental health services?
Yes, many private health insurance plans in Canada cover mental health services, such as therapy or counseling. However, coverage limits can vary, so it’s important to check the details of your plan.
Can personal health insurance be used to cover prescription medications?
Yes, private health insurance in Canada can help cover the cost of prescription medications, especially for those not fully covered by provincial health plans. While provincial healthcare plans generally cover medically necessary prescriptions for specific groups (e.g., seniors or those on social assistance), private insurance can fill in the gaps for other medications that might not be covered under the public system.
How can I apply for private health insurance in Canada?
To apply for private health insurance in Canada, we recommend scheduling a call with one of our experienced advisors. Our advisors compare quotes, plans, and help you select the best health insurance plan that meets your needs.
Canadian private health insurance covers a range of additional healthcare services not included in provincial healthcare plans, such as dental care, vision care, and prescription medications. It also covers mental health services, paramedical treatments, and emergency medical coverage outside Canada. This supplemental coverage allows Canadians to access comprehensive healthcare beyond what the public system offers.